题目描述
A wireless sensor network consists of autonomous sensors scattered in an environment where they monitor conditions such as temperature, sound, and pressure.
Samantha is a researcher working on the Amazon Carbon-dioxide Measurement (ACM) project. In this project, a wireless sensor network in the Amazon rainforest gathers environmental information. The Amazon rainforest stores an amount of carbon equivalent to a decade of global fossil fuel emissions, and it plays a crucial role in the world’s oxygen-transfer processes. Because of the huge size of this forest, changes in the forest affect not only the local environment but also global climate by altering wind and ocean current patterns. The goal of the ACM project is to help scientists better understand earth’s complex ecosystems and the impact of human activities.
Samantha has an important hypothesis and to test her hypothesis, she needs to find a subset of sensors in which each pair of sensors can communicate directly with each other. A sensor can communicate directly with any other sensor having distance at most \(d\) from it. In order for her experiments to be as accurate as possible, Samantha wants to choose as many sensors as possible.
As one does not simply walk into the Amazon, Samantha cannot add new sensors or move those that are currently in place. So given the current locations of the sensors, she needs your help to find the largest subset satisfying her criteria. For simplicity, represent the location of each sensor as a point in a two-dimensional plane with the distance between two points being the usual Euclidean distance.
输入格式
The input consists of a single test case. The first line contains two integers \(n\) and \(d\) (\(1 \le n \le 100\) and \(1 \le d \le 10\, 000\)), where \(n\) is the number of sensors available and \(d\) is the maximum distance between sensors that can communicate directly. Sensors are numbered \(1\) to \(n\). Each of the next \(n\) lines contains two integers \(x\) and \(y\) (\(-10\, 000\le x, y \le 10\, 000\)) indicating the sensor coordinates, starting with the first sensor.
求最大独立集,首先可以用爆搜/随机化(模拟退火)
然后来看正常解法。
直接做是很难做的,考虑枚举两个最远点。然后就有了这样一幅图。
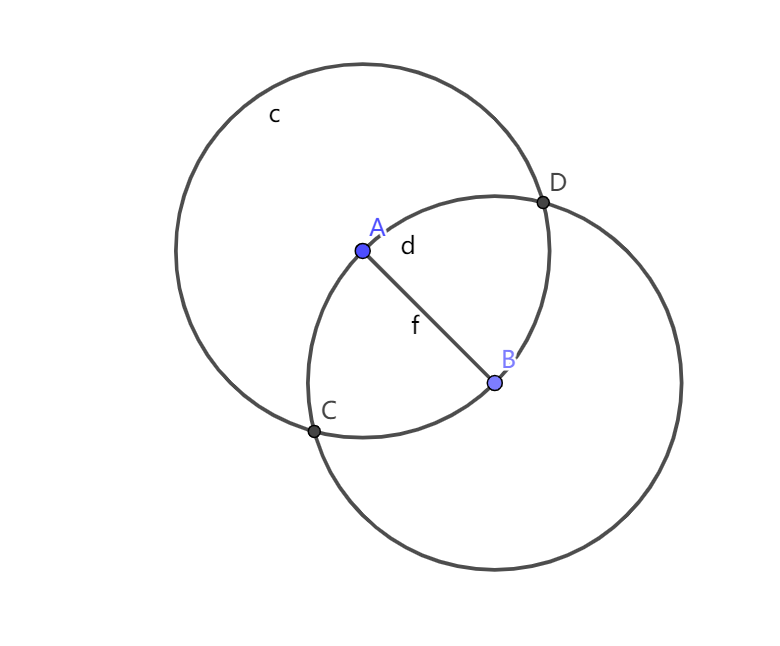
只有不规则图形 ADB 和 ABC 中的点可能被选上。
然后 用初中数学 分析一下发现,如果将所有大于 \(d\) 的可选点连边,是一个二分图。因为只有在直线两边的点会连起来。
然后就是求二分图最大独立集的问题了。
理论复杂度 \(O(n^{4.5})\),理论上还可以除以 \(\omega\),但是本身常数就很小所以不用。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=105;
int n,d,vs[N],v[N][N],c,st[N],p[N],l,r,q[N],mx,k,mm[N],f[N][N];
struct node{
int x,y;
}t[N];
int dis(node x,node y)
{
return (x.x-y.x)*(x.x-y.x)+(x.y-y.y)*(x.y-y.y);
}
void dfs(int x,int y)
{
if(!~vs[x])
{
vs[x]=y;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(v[x][i])
dfs(i,y^1);
}
}
int bfs()
{
memset(p,0,sizeof(p));
memset(mm,0,sizeof(mm));
p[q[l=r=1]=0]=1;
while(l<=r)
{
for(int i=0;i<=n+1;i++)
if(!p[i]&&v[q[l]][i])
p[q[++r]=i]=p[q[l]]+1;
++l;
}
return p[n+1];
}
int sou(int x)
{
if(x==n+1)
return 1;
for(int&i=mm[x];i<=n+1;i++)
{
if(v[x][i]&&p[i]==p[x]+1&&sou(i))
{
v[x][i]=0,v[i][x]=1;
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d%d",&n,&d);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
scanf("%d%d",&t[i].x,&t[i].y);
st[mx=1]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(int j=1;j<i;j++)
{
memset(v,0,sizeof(v));
memset(vs,-1,sizeof(vs));
int k=dis(t[i],t[j]);
c=0;
if(k>d*d)
continue;
for(int a=1;a<=n;a++)
{
if(dis(t[i],t[a])>k||dis(t[j],t[a])>k)
continue;
for(int b=1;b<=n;b++)
if(dis(t[b],t[j])<=k&&dis(t[b],t[i])<=k&&dis(t[a],t[b])>k&&a^b)
v[a][b]=1;
}
for(int a=1;a<=n;a++)
if(dis(t[i],t[a])<=k&&dis(t[j],t[a])<=k&&!~vs[a])
dfs(a,0);
for(int a=1;a<=n;a++)
{
if(vs[a]==0)
v[0][a]=1,++c;
else if(vs[a]==1)
{
for(int b=1;b<=n;b++)
v[a][b]=0;
v[a][n+1]=1,++c;
}
}
memcpy(f,v,sizeof(f));
int g=0,ans=0,tp=0;
while(bfs())
while(g=sou(0))
ans+=g;
if(c-ans>mx)
{
mx=c-ans;
for(int a=1;a<=n;a++)
if(vs[a]==0&&p[a]||vs[a]==1&&!p[a])
st[++tp]=a;
}
}
}
printf("%d\n",mx);
for(int i=1;i<=mx;i++)
printf("%d ",st[i]);
}