A - Double Click
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int32_t main() {
int n , d;
cin >> n >> d;
vector<int> a(n);
for( auto & i : a ) cin >> i;
for( int i = 1 ; i < n ; i ++ ){
if( a[i] - a[i-1] <= d ){
cout << a[i];
return 0;
}
}
cout << "-1\n";
return 0;
return 0;
}
B - chess960
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int32_t main() {
string s;
cin >> s;
vector<int> v;
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ){
if( s[i] == 'B' ) v.push_back(i);
}
if( v[0] % 2 == v[1] % 2 ){
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
v.clear();
for( int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; i ++ ){
if( s[i] == 'K' || s[i] == 'R' )
v.push_back(i);
}
if( s[ v[0] ] != s[ v[2] ] ){
cout << "No\n";
return 0;
}
cout << "Yes\n";
}
C - PC on the Table
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int32_t main() {
int n , m;
string s;
cin >> n >> m;
while( n -- ){
cin >> s;
for( int i = 1 ; i < m ; i ++ ){
if( s[i] == 'T' && s[i-1] == 'T' )
s[i-1] = 'P' , s[i] = 'C';
}
cout << s << "\n";
}
}
D - Count Subtractions
过程其实不难理解,反复的做减法直到大小关系改变着可以直接用取模来代替。不过要注意出现倍数的情况,此事要少减一次。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int32_t main() {
int a, b , cnt = 0;
cin >> a >> b;
while (a != b) {
if( a > b ) cnt += a / b , a %= b;
else cnt += b / a , b %= a;
if( min( a , b ) == 0 ) cnt -- , a = b;
}
cout << cnt;
}
E - Kth Takoyaki Set
我的写法其实蛮暴力的,用 set 维护前\(k\)小,在维护一个由之前的数产生的数的集合,每次选一个最小的加入到前\(k\)小中。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
int read(){
int x = 0 , f = 1 , ch = getchar();
while( (ch < '0' || ch > '9') && ch != '-' ) ch = getchar();
if( ch == '-' ) f = -1 , ch = getchar();
while( ch >= '0' && ch <= '9' ) x = ( x << 3 ) + ( x << 1 ) + ch - '0' , ch = getchar();
return x * f;
}
int32_t main() {
int n = read() , k = read();
vector<int> a(n);
set<int>b , c;
for( int & i : a ) i = read() , b.insert(i);
for( int x ;c.size() < k ; ){
x = *b.begin() , b.erase(x);
c.insert(x);
for( auto i : a ){
if( c.count( i + x ) == 0 ) b.insert( i + x );
}
}
cout << *c.rbegin() << "\n";
}
F - Minimum Bounding Box 2
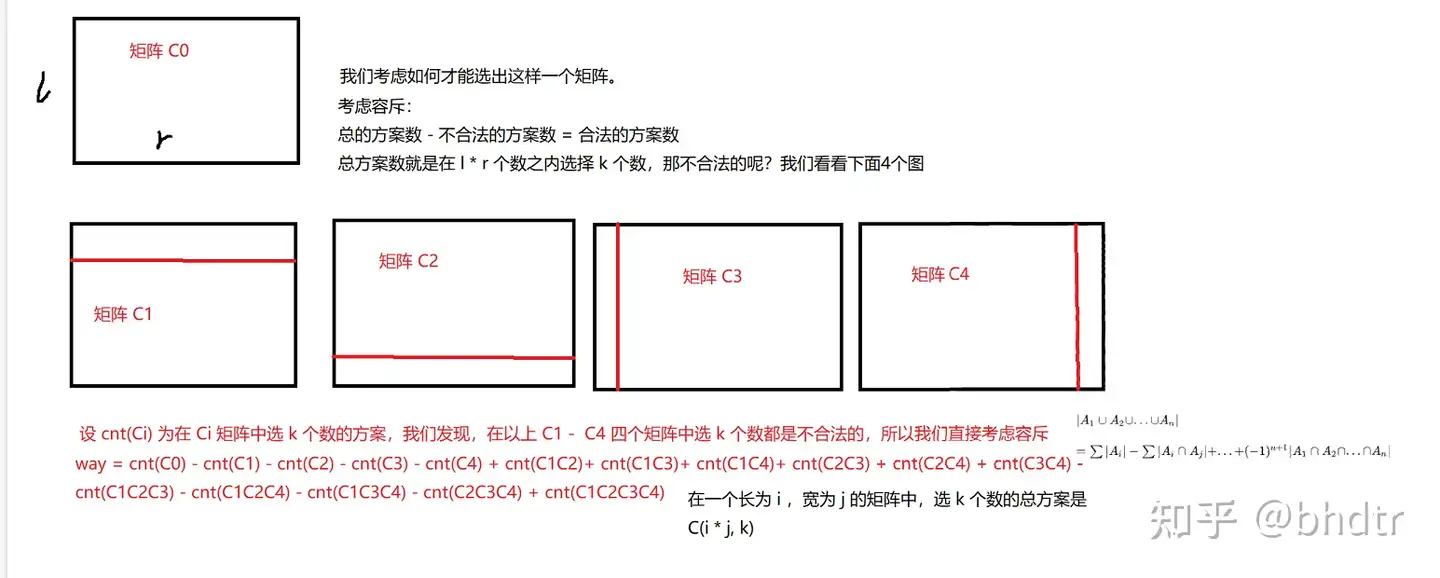
其实就是枚举一下矩形的大小,然后计算出这么大的矩形的贡献,计算贡献采用的是容斥原理。
荣斥可以参考下面的图片,计算方法可以直接用下面这个式子。
\[cnt( l\times r) \\
- 2cnt((l-1)\times r)-2cnt(l\times (r-1))\\
+ cnt((l-2)\times r) +cnt(l\times(r-2)) + 4cnt((l-1)\times (r-1)) \\
- 2cnt((l-1)\times(r-2)) - 2cnt((l-2)\times(r-1))\\
+ cnt((l-2)\times(r-2))
\]
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
const int N = 1e6 + 5, mod = 998244353;
int fact[N], invFact[N];
int power(int x, int y) {
int ans = 1;
while (y) {
if (y & 1) ans = ans * x % mod;
y >>= 1, x = x * x % mod;
}
return ans;
}
int inv(int x) {
return power(x, mod - 2);
}
int C(int x, int y) {
if (x < y) return 0;
return fact[x] * invFact[x - y] % mod * invFact[y] % mod;
}
void init() {
fact[0] = 1, invFact[0] = inv(1);
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++)
fact[i] = fact[i - 1] * i % mod, invFact[i] = inv(fact[i]);
return;
}
int32_t main() {
init();
int n, m, k;
cin >> n >> m >> k;
if (k == 1) {
cout << "1\n";
return 0;
}
int ans = 0, cnt;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++) {
cnt = 0;
for (int u = 0; u <= 2; u++)
for (int v = 0; v <= 2; v++) {
cnt += C((i - u) * (j - v), k) * (v == 1 ? -2 : 1) * (u == 1 ? -2 : 1);
cnt = (cnt % mod + mod) % mod;
}
ans = (ans + i * j % mod * (n - i + 1) % mod * (m - j + 1) % mod * cnt % mod) % mod;
}
cout << ans * inv(C(n * m, k)) % mod;
return 0;
}
- Beginner AtCoder Contest 297beginner atcoder contest 297 297 beginner bounding atcoder contest programming beginner atcoder beginner atcoder contest 296 beginner atcoder contest 295 beginner atcoder contest abcde beginner atcoder contest 335 beginner atcoder contest 332 beginner atcoder contest 328 beginner atcoder contest 315