Nature of SEE
Definition of SEE
Software Engineering Economics
The application of economic theory and methods to software engineering business decision-making. As such it can be seen as a means to an end by managers, in terms of finding the most efficient way of allocating their scarce resources and
reaching their objectives.
Related theoretical foundations
- Theory of software engineering (foundation)
- Economic theory (foundation)
- Decision science (tool)
- Business theory (metrics)
- Project management (process)
Economic theory
essentially an approach that
treats the individual elements within the economy (consumers, firms and workers) as rational agents with objectives that can be expressed as quantitative functions (utilities and profits) that are to be optimized, subject to certain quantitative constraints.
- Positive statements are factual statements whose truth or falsehood can be verified by empirical study or logic.
- Normative statements involve a value judgement and cannot be verified by empirical study or logic.
Decision science
The most important aspects are as follows:
- Numerical and algebraic analysis.
- Optimization.
- Statistical estimation and forecasting.
- Analysis of risk and uncertainty
- Time-value-of-money techniques.
Business theory
All firms consist of organizations that are divided structurally into different departments or units.
Typically, the units involved are:
- Production and operations
- Marketing
- Finance and accounting
- Human resources
Problem-Model-Method
structure of research
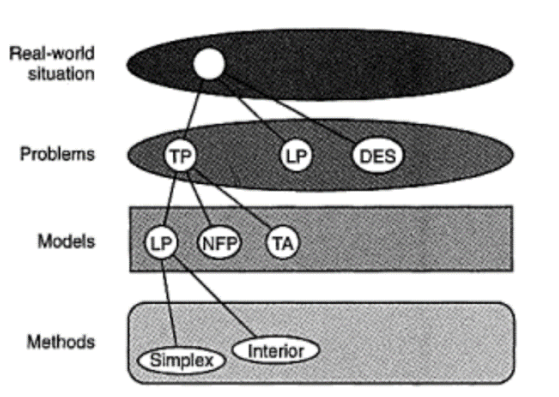
Principles
- Optimization
- Allocation
- Verification
Optimization (优化)
- Trade-offs and Budget Constraints
All optimization problems involve trade-offs. Economists use budget constraints to describe trade-offs.
budget constraint(预算约束) is the set of things that a person can choose to do (or buy) without breaking her budget. - Cost-Benefit Analysis
a calculation that identifies the best option by summing
benefits and subtracting costs.
Cost-benefit analysis is used to identify the alternative that has the greatest net benefit, which is the sum of the benefits of choosing an alternative minus the sum of the costs of choosing that alternative.
Allocation (分配)
Equilibrium(均衡) is the special situation in which everyone is trying to optimize, so nobody believes that they would benefit personally by changing his or her own behavior.
Verification (验证)
Economists test their ideas with data. We refer to such evidence-based analysis as empirical analysis or empiricism.