x86开机
参考于:【哈工大】操作系统 李治军、linux-0.11源码。
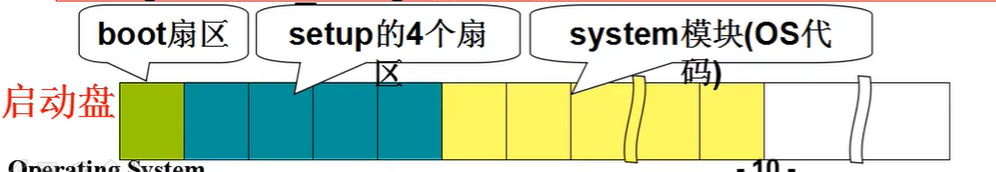
需要读入执行的内容有:boot扇区中的bootsect、setup和system。源文件处于启动盘中排在前面扇区:
上电时
刚开机时处于实模式。CS=0xFFFF、IP=0x0000。寻址0xFFFF0(ROM BIOS映射区)。这里执行检查RAM、键盘、显示器、软硬磁盘,并将引导扇区(磁盘0磁道0扇区)读入0x7C00处。然后设置CS=0x07C0、IP=0x0000。执行载入的引导扇区代码。
以下代码只列出了部分。
bootsect.s
SYSSIZE = 0x3000 ! system模块大小
SETUPLEN = 4 ! setup扇区数
BOOTSEG = 0x07c0 ! bootsector原始地址
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! bootsector移动的目标地址
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! setup地址
SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system加载位置
ENDSEG = SYSSEG + SYSSIZE ! where to stop loading
entry _start ! 程序入口为_start
首先,_start函数将0x07C00下的bootsect复制到0x90000后,目的是腾出空间给OS中的system模块。然后跳转到该地址执行go:
_start:
! 初始化DS、ES、SI、DI,并把CX设置为扇区大小。
mov ax,#BOOTSEG
mov ds,ax
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
mov cx,#256
sub si,si
sub di,di
! 复制DS:SI内容到ES:DI,即bootsect的256字(512字节)。
rep
movw
! IP置go,CS置INITSEG,并跳转执行。
jmpi go,INITSEG
bootsect扇区后紧临的4个扇区是setup,需要将其读入到SETUPSEG(load_setup),然后打印信息,加载system到0x10000(临时放置的地址,在setup中会被移动到0x0处):
go: mov ax,cs
mov ds,ax
mov es,ax
mov ss,ax
mov sp,#0xFF00 ! arbitrary value >>512
! 读入setup的4个扇区。0x13是BIOS读磁盘扇区的中断,AH=0x02读磁盘,AL=0x04扇区数,CH=0x00柱面号,CL=0x02开始扇区,DH=0x00磁头号,DL=0x00驱动器号,ES:BX=0x90200内存地址。
load_setup:
mov dx,#0x0000
mov cx,#0x0002
mov bx,#0x0200
mov ax,#0x0200+SETUPLEN
int 0x13
jnc ok_load_setup ! ok - continue
mov dx,#0x0000
mov ax,#0x0000 ! reset the diskette
int 0x13
j load_setup
ok_load_setup:
! 获取磁盘驱动器参数,特别是扇区/磁道数。
mov dl,#0x00
mov ax,#0x0800 ! AH=8 is get drive parameters
int 0x13
mov ch,#0x00
seg cs
mov sectors,cx
mov ax,#INITSEG
mov es,ax
! 打印一些信息,0x10是BIOS的显示字符中断,BP指出字符地址。
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos
xor bh,bh
int 0x10
mov cx,#24
mov bx,#0x0007 ! page 0, attribute 7 (normal)
mov bp,#msg1
mov ax,#0x1301 ! write string, move cursor
int 0x10
! 使用read_it读入system。
mov ax,#SYSSEG
mov es,ax ! segment of 0x010000
call read_it
...
! 跳转到0x9020:0x0000执行setup。
jmpi 0,SETUPSEG
...
msg1:
.byte 13,10
.ascii "Loading system ..."
.byte 13,10,13,10
setup.s
setup将完成OS启动前的设置。
INITSEG = 0x9000 ! we move boot here - out of the way
SYSSEG = 0x1000 ! system loaded at 0x10000 (65536).
SETUPSEG = 0x9020 ! this is the current segment
entry start
start先设置一些信息,除了下面的光标地址、内存大小,还有显卡参数(0x9000C)、根设备号(0x901FC)等。
start:
! 使用BIOS的0x10中断,取出光标地址放在0x90000处。
mov ax,#INITSEG ! this is done in bootsect already, but...
mov ds,ax
mov ah,#0x03 ! read cursor pos
xor bh,bh
int 0x10 ! save it in known place, con_init fetches
mov [0],dx ! it from 0x90000.
! 使用BIOS的0x15中断,取出内存大小放在0x90002处。
mov ah,#0x88
int 0x15
mov [2],ax
...
然后,进入保护模式(开机时是实模式):
! now we want to move to protected mode ...
cli ! 不允许中断
! 首先,把system移动到真实的地址0x00000处。
mov ax,#0x0000
cld ! 'direction'=0, movs moves forward
do_move:
mov es,ax ! ES置0x0000
add ax,#0x1000
cmp ax,#0x9000
jz end_move
mov ds,ax ! DS置0x1000
sub di,di
sub si,si
mov cx,#0x8000 ! 移动大小为0x8000字节
rep
movsw
jmp do_move
! 然后,加载段描述符。
end_move:
mov ax,#SETUPSEG ! right, forgot this at first. didn't work :-)
mov ds,ax
lidt idt_48 ! load idt with 0,0
lgdt gdt_48 ! load gdt with whatever appropriate
! 启动A20总线。
call empty_8042
mov al,#0xD1 ! command write
out #0x64,al
call empty_8042
mov al,#0xDF ! A20 on
out #0x60,al
call empty_8042
! 重新编程中断。
...
! 最终,设置保护模式。这里将CR0的PE置1,然后使用jumpi指令,IP置0,CS根据gdt表获取,8指定之下为0,即跳转到0x00000000处,也就是system处执行。
mov ax,#0x0001 ! protected mode (PE) bit
lmsw ax ! This is it!
jmpi 0,8 ! jmp offset 0 of segment 8 (cs)
! This routine checks that the keyboard command queue is empty
! No timeout is used - if this hangs there is something wrong with
! the machine, and we probably couldn't proceed anyway.
empty_8042:
.word 0x00eb,0x00eb
in al,#0x64 ! 8042 status port
test al,#2 ! is input buffer full?
jnz empty_8042 ! yes - loop
ret
gdt:
.word 0,0,0,0 ! dummy
.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb)
.word 0x0000 ! base address=0
.word 0x9A00 ! code read/exec
.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386
.word 0x07FF ! 8Mb - limit=2047 (2048*4096=8Mb)
.word 0x0000 ! base address=0
.word 0x9200 ! data read/write
.word 0x00C0 ! granularity=4096, 386
idt_48:
.word 0 ! idt limit=0
.word 0,0 ! idt base=0L
gdt_48:
.word 0x800 ! gdt limit=2048, 256 GDT entries
.word 512+gdt,0x9 ! gdt base = 0X9xxxx
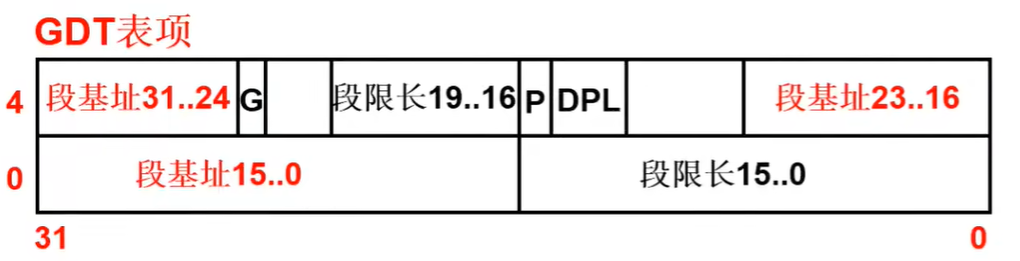
GDT表项格式如下,在jumpi 0,8中,CS选择子为8,查gdt表项对应0x07FF、0x0000、0x9A00、0x00C0,放入表项,对应的段基址为0。
system
system模块由许多文件编译而成,第一部分是head.s。
head.s
startup_32:
# 指向gdt的0x10项(数据段)
movl $0x10,%eax
mov %ax,%ds
mov %ax,%es
mov %ax,%fs
mov %ax,%gs
# 设置系统栈
lss stack_start,%esp
# 这里又一次设置了idt和gdt表,setup中设置idt和gdi表的目的只是用于跳转到system模块执行,而system中执行需要新的idt和gdt表。
call setup_idt
call setup_gdt
...
jmp after_page_tables
调用setup_paging来设置页表,RET后,执行main函数,前面压栈的是3个main的参数,为0。还压入了L6这个死循环函数,但main函数永远不会退出,所以L6永远不会执行。
after_page_tables:
pushl $0 # These are the parameters to main :-)
pushl $0
pushl $0
pushl $L6 # return address for main, if it decides to.
pushl $main # main函数压栈。
jmp setup_paging # 设置页表.
L6:
jmp L6
...
main.c
mem_init(main_memory_start,memory_end); // 主内存区初始化。mm/memory.c
trap_init(); // 陷阱门(硬件中断向量)初始化,kernel/traps.c
blk_dev_init(); // 块设备初始化,kernel/blk_drv/ll_rw_blk.c
chr_dev_init(); // 字符设备初始化, kernel/chr_drv/tty_io.c
tty_init(); // tty初始化, kernel/chr_drv/tty_io.c
time_init(); // 设置开机启动时间 startup_time
sched_init(); // 调度程序初始化(加载任务0的tr,ldtr)(kernel/sched.c)
// 缓冲管理初始化,建内存链表等。(fs/buffer.c)
buffer_init(buffer_memory_end);
hd_init(); // 硬盘初始化,kernel/blk_drv/hd.c
floppy_init(); // 软驱初始化,kernel/blk_drv/floppy.c
sti(); // 所有初始化工作都做完了,开启中断
// 下面过程通过在堆栈中设置的参数,利用中断返回指令启动任务0执行。
move_to_user_mode(); // 移到用户模式下执行
if (!fork()) { /* we count on this going ok */
init(); // 在新建的子进程(任务1)中执行。
}