题目链接:星之河
比较经典的偏序问题。区别于强制在线类算法:树套树之类的,对于偏序问题,我们有许多种优秀的离线算法,比如此篇要讲的 cdq 分治。
它更偏向于一种思想,它的思想使得它对偏序类问题,往往都有一种非常好的效果。首先来看一张图。
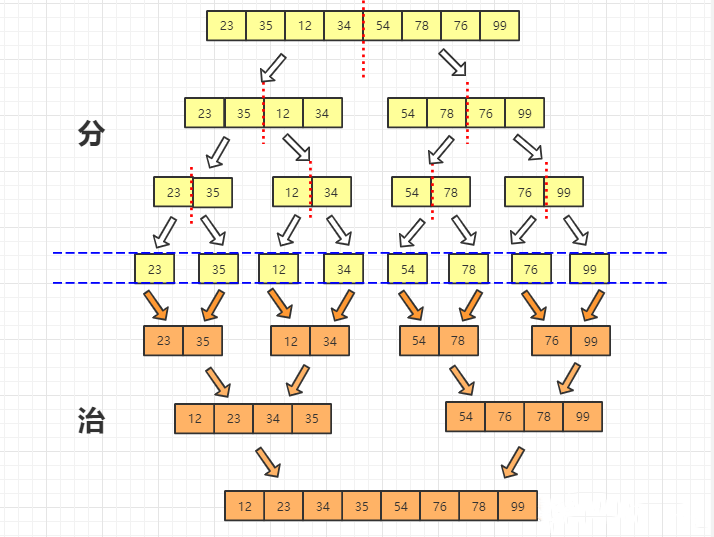
这是所有算法入门选手都会接触的归并排序的过程图。我们考虑两个过程,一个是向下不断分解到小区间,最终长度为 \(1\) 的区间开始往上合并。容易发现,对于排序类问题,我们常常来说可以至少优化掉一维,比如对第一维进行有序排序。那么很容易观察到此时此刻的两个需要合并的区间: \([l,mid]\) 与 \([mid+1,r]\) 它们之间有一个很明显的关系,那就是第一维因为是有序的,那么左区间的所有的第一维一定是 \(\le\) 右区间的第一维的。此时此刻,我们可以考虑左区间对右区间的贡献,考虑完毕以后,他们组成了新的:
- 左区间对下一个右区间作为贡献。
- 右区间统计其他左区间对它的贡献。
这个就是 cdq 分治的核心思想:在归并的过程中,统计左区间对右区间的影响即可。偏序类问题常常都是一个方向的,例如 \(x_i \le x_j \ (i<j)\),只需要考虑 \(i\) 对 \(j\) 的贡献即可,也就是左边的点对右边的点的贡献性,很符合 cdq 分治模型。
三维偏序从暴力到正解
考虑枚举右区间的每个端点,暴力地统计每个点剩下两维是否能对当前点造成贡献,这个复杂度显然是很高的。考虑优化,我们如果左右区间的第二维在自身的区间内是有序的,那么很显然我们可以用双指针算法,很容易的找到对于右区间的某个点应该有左区间哪部分影响到。这部分本质上抽象出来就是这么个东西:
这个很简单吧,跑双指针轻松实现。那么第二维我们就可以去掉了,最后就是一个很简单的贡献区域查询。比如我们将 \(1 \sim left_i\) 对应的第三维加入贡献中,考虑当前点 \(right_i\) 需要的贡献范围就行了,带修的数据结构都行。基础树状数组比较常用。
来解决下如何让第二维有序,别忘了我们本质上的结构是“归并排序”,归并排序的核心操作就是在归并时完成:
当然了,实际情景如果懒得写这个 \(merge\) 可以考虑直接调稳定排序的函数,因为基本接近有序了,这部分常数并不是很大。对此,我们的三维偏序就暂时讲到这。
本题核心转化,对于一个子树类型的题,我们常常会使用 dfs 序将其转化为区间上的问题,容易知道,处理出一个 dfs序 以后,很容易通过区间查找 \([s_{curr},e_{curr}]\) 找出这部分的贡献。我们常见的计数类型题可以考虑用树状数组前缀和做差实现。
那么核心点就是处理出 dfs 序以后转化为这样一个问题:
对于两个点 \(i\) 与 \(j\):
- \(A_i \le A_j\)
- \(B_i \le B_j\)
- \(s_{i} \le s_j \le e_i,其中s_i 是dfs序起点,e_i则是终点\)
那么很显然的一个 cdq 分治求偏序问题。
最后的细节
首先呢,怎么处理 dfs 序因个人而已,有人喜欢终点也加一,那么对应的查询范围也需要有所更改。
其次呢,对于 cdq 分治而言,最容易错的地方,莫过于考虑当相等时该如何排序了。这点是必须去具体考虑的。例如本题而言,你要注意到一点,当 \(A_i 和 B_i\) 都相等的两个偏序对,你应该考虑谁对谁的影响,注意 cdq 分治只考虑左边对右边的影响,所以只能一方对一方产生影响。很容易知道,第三维 dfs 序越小的越可能是根,否则如果这两个点是同棵子树,而前者恰好又是根,你还是按照原本的 dfs 序以升序排列,那么很显然,根对子树无影响,漏算了子树对根的影响,所以这里排序记得手写一下。
最后就是有无手写 merge 的两个版本代码,不过其实 c++ 也有自带的 merge 函数可以调用,不过照顾其他语言选手还是手写出来。
无merge参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
// #define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three > other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 2e5 + 10;
vector<int> child[N];
int s[N], e[N], tot;
//Ai、Bi、i
T3<int, int, int> t[N];
int siz;
inline void dfs(const int curr, const int fa)
{
s[curr] = ++tot;
for (const auto nxt : child[curr])if (nxt != fa)dfs(nxt, curr);
e[curr] = tot;
}
int n;
int ans[N];
int bit[N];
//注意到需要保留子树对根的影响,子树应该在左边
inline bool cmpA(const T3<int, int, int>& x, const T3<int, int, int> y)
{
if (x.one != y.one)return x.one < y.one;
if (x.tow != y.tow)return x.tow < y.tow;
return s[x.three] > s[y.three];
}
inline bool cmpB(const T3<int, int, int>& x, const T3<int, int, int> y)
{
return x.tow < y.tow;
}
inline void add(int x, const int val)
{
for (; x <= n; x += lowBit(x))bit[x] += val;
}
inline int query(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowBit(x))ans += bit[x];
return ans;
}
inline int Query(const int l, const int r)
{
return query(r) - query(l - 1);
}
inline void cdq(const int L, const int R)
{
const int mid = L + R >> 1;
if (L == R)return;
cdq(L, mid), cdq(mid + 1, R);
//去掉B的影响
stable_sort(t + L, t + mid + 1, cmpB);
stable_sort(t + mid + 1, t + R + 1, cmpB);
//基本双指针
int l = L;
forn(r, mid+1, R)
{
int queryPoint = t[r].three;
for (; l <= mid and t[l].tow <= t[r].tow; l++)add(s[t[l].three], 1);
ans[queryPoint] += Query(s[queryPoint], e[queryPoint]); //区间查询子树区间贡献
}
//清空用于下次计算
forn(i, L, l-1)add(s[t[i].three], -1);
}
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 1, n-1)
{
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
child[u].push_back(v);
child[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0); //处理dfs序
forn(i, 1, n)
{
auto& [A,B,id] = t[i];
cin >> A >> B, id = i;
}
//去掉A的影响
sort(t + 1, t + n + 1, cmpA);
cdq(1, n);
forn(i, 1, n)if (ans[i])cout << ans[i] << endl;
}
signed int main()
{
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
}
有merge参照代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
//#pragma GCC optimize("Ofast,unroll-loops")
// #define isPbdsFile
#ifdef isPbdsFile
#include <bits/extc++.h>
#else
#include <ext/pb_ds/priority_queue.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tree_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/trie_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/tag_and_trait.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/hash_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/list_update_policy.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/assoc_container.hpp>
#include <ext/pb_ds/exception.hpp>
#include <ext/rope>
#endif
using namespace std;
using namespace __gnu_cxx;
using namespace __gnu_pbds;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef pair<int, int> pii;
typedef pair<ll, ll> pll;
typedef tuple<int, int, int> tii;
typedef tuple<ll, ll, ll> tll;
typedef unsigned int ui;
typedef unsigned long long ull;
typedef __int128 i128;
#define hash1 unordered_map
#define hash2 gp_hash_table
#define hash3 cc_hash_table
#define stdHeap std::priority_queue
#define pbdsHeap __gnu_pbds::priority_queue
#define sortArr(a, n) sort(a+1,a+n+1)
#define all(v) v.begin(),v.end()
#define yes cout<<"YES"
#define no cout<<"NO"
#define Spider ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);cout.tie(nullptr);
#define MyFile freopen("..\\input.txt", "r", stdin),freopen("..\\output.txt", "w", stdout);
#define forn(i, a, b) for(int i = a; i <= b; i++)
#define forv(i, a, b) for(int i=a;i>=b;i--)
#define ls(x) (x<<1)
#define rs(x) (x<<1|1)
#define endl '\n'
//用于Miller-Rabin
[[maybe_unused]] static int Prime_Number[13] = {0, 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
template <typename T>
int disc(T* a, int n)
{
return unique(a + 1, a + n + 1) - (a + 1);
}
template <typename T>
T lowBit(T x)
{
return x & -x;
}
template <typename T>
T Rand(T l, T r)
{
static mt19937 Rand(time(nullptr));
uniform_int_distribution<T> dis(l, r);
return dis(Rand);
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
T1 modt(T1 a, T2 b)
{
return (a % b + b) % b;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename T3>
T1 qPow(T1 a, T2 b, T3 c)
{
a %= c;
T1 ans = 1;
for (; b; b >>= 1, (a *= a) %= c)if (b & 1)(ans *= a) %= c;
return modt(ans, c);
}
template <typename T>
void read(T& x)
{
x = 0;
T sign = 1;
char ch = getchar();
while (!isdigit(ch))
{
if (ch == '-')sign = -1;
ch = getchar();
}
while (isdigit(ch))
{
x = (x << 3) + (x << 1) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
x *= sign;
}
template <typename T, typename... U>
void read(T& x, U&... y)
{
read(x);
read(y...);
}
template <typename T>
void write(T x)
{
if (typeid(x) == typeid(char))return;
if (x < 0)x = -x, putchar('-');
if (x > 9)write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 ^ 48);
}
template <typename C, typename T, typename... U>
void write(C c, T x, U... y)
{
write(x), putchar(c);
write(c, y...);
}
template <typename T11, typename T22, typename T33>
struct T3
{
T11 one;
T22 tow;
T33 three;
bool operator<(const T3 other) const
{
if (one == other.one)
{
if (tow == other.tow)return three > other.three;
return tow < other.tow;
}
return one < other.one;
}
T3() { one = tow = three = 0; }
T3(T11 one, T22 tow, T33 three) : one(one), tow(tow), three(three)
{
}
};
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMax(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x < y)x = y;
}
template <typename T1, typename T2>
void uMin(T1& x, T2 y)
{
if (x > y)x = y;
}
constexpr int N = 2e5 + 10;
vector<int> child[N];
int s[N], e[N], tot;
T3<int, int, int> t[N];
int siz;
inline void dfs(const int curr, const int fa)
{
s[curr] = ++tot;
for (const auto nxt : child[curr])if (nxt != fa)dfs(nxt, curr);
e[curr] = tot;
}
int n;
int ans[N];
int bit[N];
//注意保留子树对根的影响,让子树在左边即可
inline bool cmpA(const T3<int, int, int>& x, const T3<int, int, int> y)
{
if (x.one != y.one)return x.one < y.one;
if (x.tow != y.tow)return x.tow < y.tow;
return s[x.three] > s[y.three];
}
inline bool cmpB(const T3<int, int, int>& x, const T3<int, int, int> y)
{
return x.tow < y.tow;
}
inline void add(int x, const int val)
{
for (; x <= n; x += lowBit(x))bit[x] += val;
}
inline int query(int x)
{
int ans = 0;
for (; x; x -= lowBit(x))ans += bit[x];
return ans;
}
inline int Query(const int l, const int r)
{
return query(r) - query(l - 1);
}
//Ai、Bi、i
T3<int, int, int> tmp[N];
//合并两个有序数组
inline void merge(const int L, const int mid, const int R)
{
int i = L, j = mid + 1;
int cnt = L;
while (i <= mid and j <= R)tmp[cnt++] = t[i].tow < t[j].tow ? t[i++] : t[j++];
while (i <= mid)tmp[cnt++] = t[i++];
while (j <= R)tmp[cnt++] = t[j++];
forn(i, L, R)t[i] = tmp[i];
}
inline void cdq(const int L, const int R)
{
const int mid = L + R >> 1;
if (L == R)return;
cdq(L, mid), cdq(mid + 1, R);
int l = L;
forn(r, mid+1, R)
{
int queryPoint = t[r].three;
for (; l <= mid and t[l].tow <= t[r].tow; l++)add(s[t[l].three], 1);
ans[queryPoint] += Query(s[queryPoint], e[queryPoint]);
}
forn(i, L, l-1)add(s[t[i].three], -1);
//去掉B的影响
merge(L, mid, R);
}
inline void solve()
{
cin >> n;
forn(i, 1, n-1)
{
int u, v;
cin >> u >> v;
child[u].push_back(v);
child[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(1, 0); //处理dfs序
forn(i, 1, n)
{
auto& [A,B,id] = t[i];
cin >> A >> B, id = i;
}
sort(t + 1, t + n + 1, cmpA); //去掉A的影响
cdq(1, n);
forn(i, 1, n)if (ans[i])cout << ans[i] << endl;
}
signed int main()
{
Spider
//------------------------------------------------------
int test = 1;
// read(test);
// cin >> test;
forn(i, 1, test)solve();
// while (cin >> n, n)solve();
// while (cin >> test)solve();
}