目录
简介
vue-router是Vue.js官方的路由插件,它和vue.js是深度集成的,适合用于构建单页面应用。
vue-router是基于路由和组件的,路由用户设定访问路径的,将路径和组件映射起来。在vue-router的单页面应用中,页面的路径的改变就是组件的切换。
官网地址:https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
安装vue-router
# 可以在创建项目时就直接安装好vue-router
# 也可以单独安装,使用下面的命令
npm install vue-router
# 第二步:在main.js中引入
import router from './router'
new Vue({
router, # 添加这一行
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
使用vue-router
配置路由的跳转,只需要在src/router/index.js目录下导入组件之后,再
import IndexView from "@/views/IndexView"; // 创建好组件之后,导入组件
const routes = [
{
path: '/index/', // 浏览器的路由
name: 'index', // 别名
component: IndexView // 对应的是哪个组件
},
]
router的方法
this.$router.push(path) // 相当于点击路由链接(可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.replace(path) // 用新路由替换当前路由(不可以返回到当前路由界面)
this.$router.back() // 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(-1) // 请求(返回)上一个记录路由
this.$router.go(1) // 请求下一个记录路由
this.$router.forward() // 前进
路由跳转
方法一 使用js控制
- 使用给按钮绑定事件的方式进行跳转
<button @click="goToLogin">点我</button>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods:{
goToLogin(){
this.$router.push('/Index') // 这样点击上面的按钮后就会跳转到index页面了
}
}
}
</script>
方法二 使用标签控制
- 使用标签的方法进行跳转
<!--写法-->
<router-link to="路由"> xxx </router-link>
<!--示例-->
<router-link to="/index"><button>点我</button></router-link>
路由跳转携带参数
方法一 使用问号携带
<router-link to="/index/?pk=1"><button>点我</button></router-link>
或
<router-link to="/index/?pk="+{{xxx}}><button>点我</button></router-link>
- 通过打印console.log(this.$route)发现,数据在query中
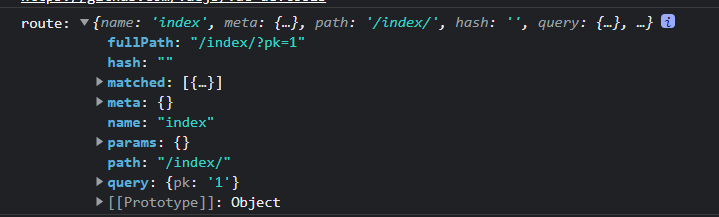
- 所以如果要取数据,可以直接使用query对象取
<script>
export default {
name: "IndexView",
created() {
console.log('route:', this.$route.query.pk)
}
}
</script>
方法二 使用斜杠分隔符携带
- 第一步 配置router目录下index.js
{
path: '/index/:pk', // 这里配置什么参数,前台传入的值对应的Key就是什么
name: 'index',
component: IndexView
},
- 第二步 配置跳转功能
<router-link to="/index/1/"><button>点我</button></router-link>
- 第三步取值
根据console.log(this.$route)可以看到,值在params中
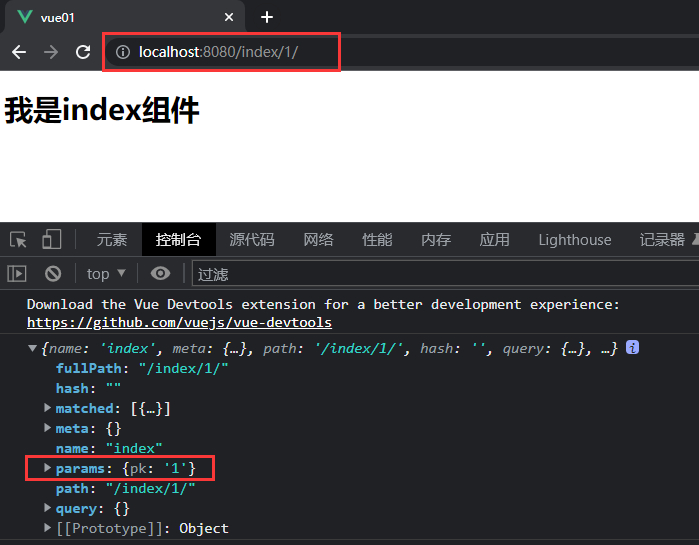
console.log(this.$route.params.pk) // 这样就可以取到值了
方法三 使用对象的方式跳转
- 可以直接在push方法中携带参数
<template>
<div class="home">
<button @click="clickFunc">点我</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
methods:{
clickFunc(){
this.$router.push({
name: 'index', // 这里的name就是router/index.js中路由配置的name别名,这个路由不需要作变化
query:{ // 可以将内容放到query中
name: 'jack',
age: '18'
},
params:{ // 可以将内容放到params中,这样路由中需要配置为path: '/index/:pk'
pk: '16',
}
})
}
}
}
</script>
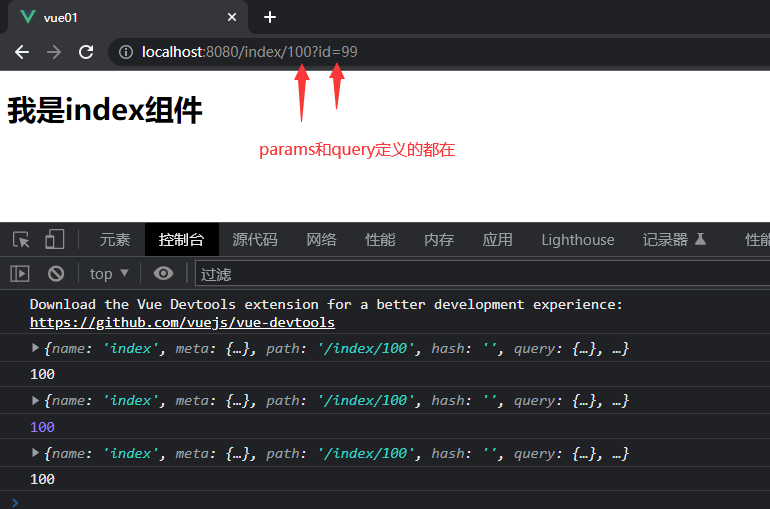
-
可以看到,使用问题携带参数的截图
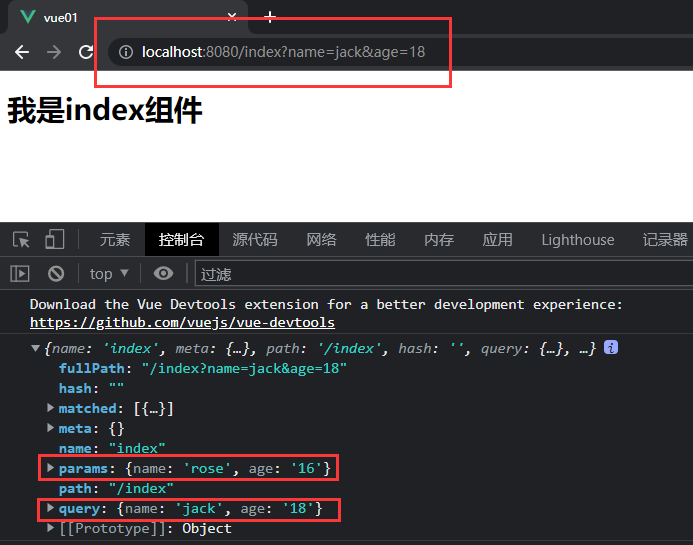
-
可以看到,使用斜杠分隔携带参数的截图
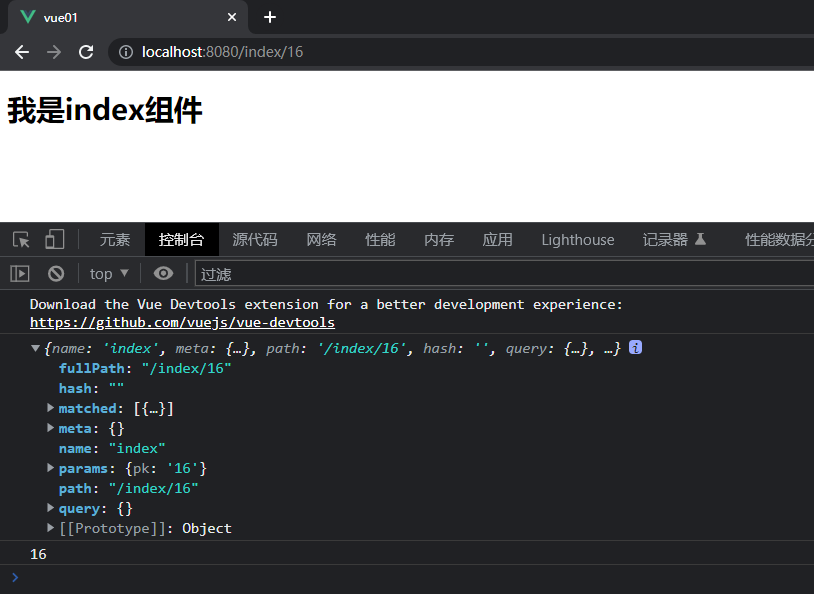
方法四 标签方式跳转携带参数
{
path: '/index/:pk', // 这里配置了:pk
name: 'index',
component: IndexView
},
<template>
<div class="home">
<!--可以定义好对象,将内容写到对象中,并在这里引用-->
<router-link :to="obj">
<button>点我</button>
</router-link>
<!--可以将跳转对象写到标签中-->
<!--如果路由配置了:pk这种分隔的方式,可以写query和params两个-->
<router-link :to="{name:'index', query:{id:99}, params:{pk:100}}">
<button>点我2</button>
</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'HomeView',
data() {
return {
obj: {
name: 'index',
query: {id: '99'},
params: {pk: '100'}
}
}
}
}
</script>
- 返回结果如下显示
router与route的区别
route # 当前页面的对象,也可以说是当前路由对象
router # new VueRouter对象,也是就是vue-router的实例
- 我们可以使用console.log查看一下这两个对象分别是什么
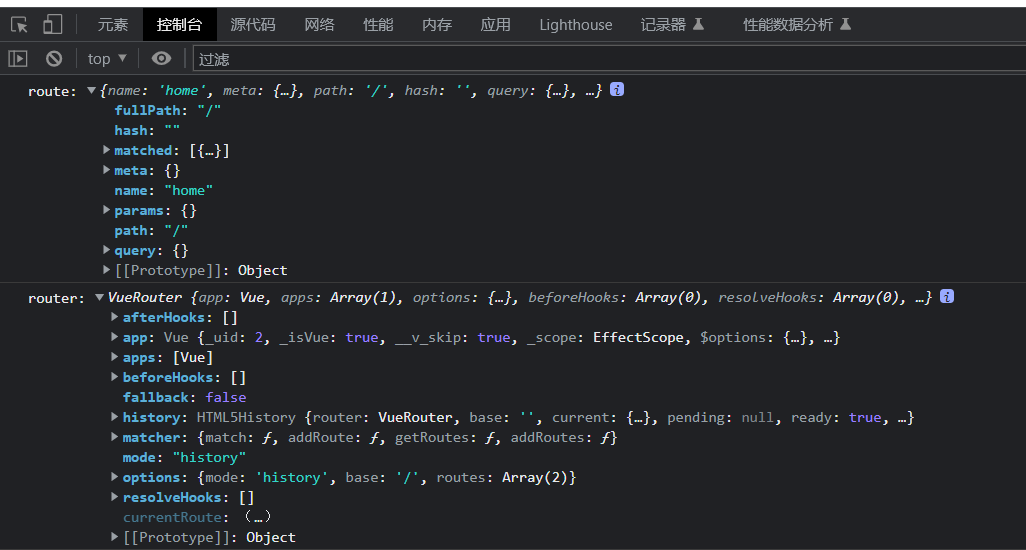
- 可以看到route对应的就是当前页面的一些信息
- router中对应的就是vue-router实例
多级路由
routes:[
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
children: [ //通过children配置子级路由
{
path: 'news', //此处一定不要写:/news 注意这个斜杠
component: News
},
{
path: 'message',//此处一定不要写:/message 注意这个斜杠
component: Message
}
]
}
]
// 跳转
< router - link
to = "/home/news" > News < /router-link>
{
path: '/demo',
component: Demo,
children: [
{
path: 'test',
component: Test,
children: [
{
name: 'hello' // 给路由定义别名
path: 'welcome',
component: Hello,
}
]
}
]
}
<!--简化前,需要写完整的路径 -->
<router-link to="/demo/test/welcome">跳转</router-link>
<!--简化后,直接通过别名跳转 -->
<router-link :to="{name:'hello'}">跳转</router-link>
<!--简化写法配合传递参数 -->
<router-link :to="{name:'hello',query:{id:666,itle:'你好'}}">跳转</router-link>
路由守卫
对路由进行权限控制,按分类分为:全局守卫(最常用),独享守卫,组件内守卫
全局路由守卫
- 前置路由守卫:在进路由前,执行代码。
- 后置路由守卫:路由跳转走,执行代码。
前置路由守卫配置
- 只需要在router/index.js文件中新增一个函数即可
router.beforeEach(
(to, from, next) => {
console.log(to, from, next)
// to 代表要去的路由
// from 代表从哪个路由跳转过来
// next 是一个函数,需要加括号执行,没有next则不会跳转到要去的路由
// 下面写一个简单的路由守卫功能
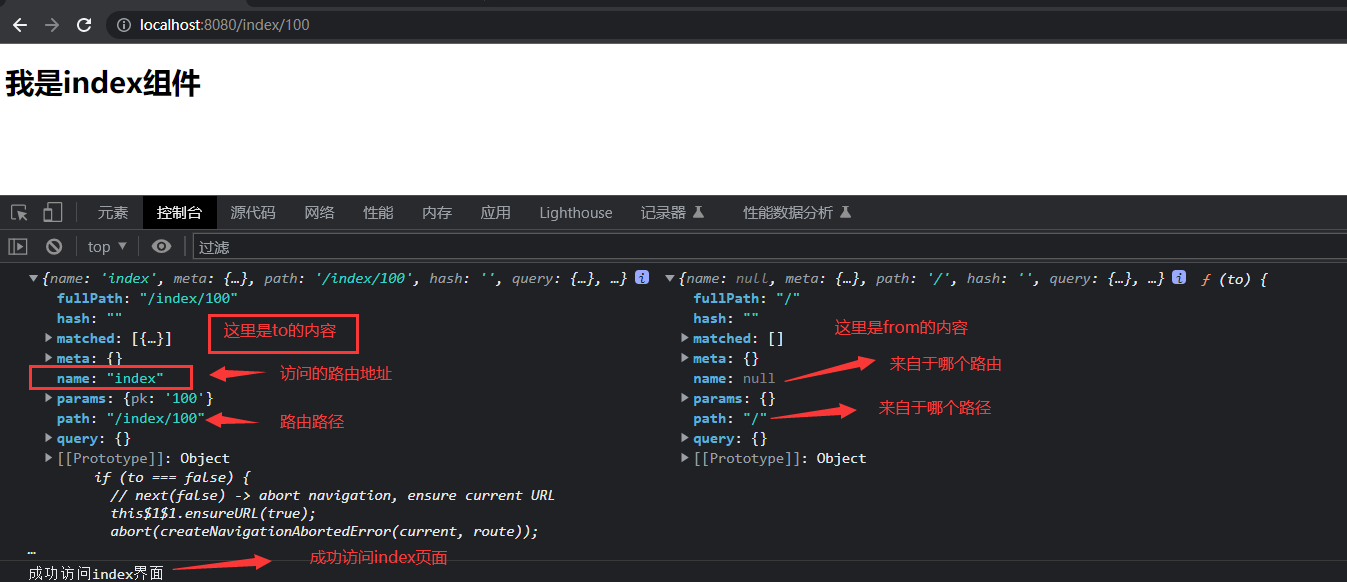
if (to.name == 'index'){
console.log('成功访问index界面')
next() // 这里不加next()是不会跳转的
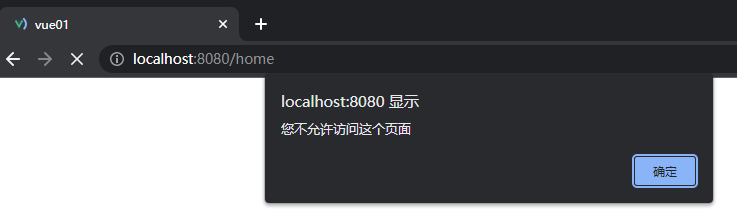
}else{
alert('您不允许访问这个页面')
}
}
)
-
访问index页面可以访问
-
访问home页面无法访问,先是弹窗,之后因为没有next()所以也不会跳转到home路由中
后置路由守卫配置
- 与前置不同的只是函数名不同,用得很少
router.afterEach((to, from)=> {
函数内容
})
独享守卫
// 该文件专门用于创建整个应用的路由器
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
//引入组件
import About from '../pages/About'
import Home from '../pages/Home'
import News from '../pages/News'
import Message from '../pages/Message'
import Detail from '../pages/Detail'
//创建并暴露一个路由器
const router = new VueRouter({
routes:[
{
name:'guanyu',
path:'/about',
component:About,
meta:{title:'关于'}
},
{
name:'zhuye',
path:'/home',
component:Home,
meta:{title:'主页'},
children:[
{
name:'xinwen',
path:'news',
component:News,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'新闻'},
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
console.log('独享路由守卫',to,from)
if(to.meta.isAuth){ //判断是否需要鉴权
if(localStorage.getItem('name')==='lqz'){
next()
}else{
alert('名不对,无权限查看!')
}
}else{
next()
}
}
},
{
name:'xiaoxi',
path:'message',
component:Message,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'消息'},
children:[
{
name:'xiangqing',
path:'detail',
component:Detail,
meta:{isAuth:true,title:'详情'},
}
]
}
]
}
]
})
export default router
组件内守卫
//进入守卫:通过路由规则,进入该组件时被调用
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
},
//离开守卫:通过路由规则,离开该组件时被调用
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
}
//通过路由规则,进入该组件时被调用
beforeRouteEnter (to, from, next) {
console.log('About--beforeRouteEnter',to,from)
if(to.meta.isAuth){ //判断是否需要鉴权
if(localStorage.getItem('school')==='atguigu'){
next()
}else{
alert('学校名不对,无权限查看!')
}
}else{
next()
}
},
//通过路由规则,离开该组件时被调用
beforeRouteLeave (to, from, next) {
console.log('About--beforeRouteLeave',to,from)
next()
}