
如果把提示词也算作一种代码的话,那么语义技能所带来的将会是全新编程方式,自然语言编程。
通常情况下一段prompt就可以构成一个Semantic Function,如此这般简单,如果我们提前可以组织好一段段prompt的管理方式,甚至可以不需要写任何的代码,就可以构造出足够多的技能来。
使用文件夹管理Semantic Function
Semantic Kernel恰好就提供了这样一种组织方式,仅需使用文本文件和文件夹就可以管理Semantic Function。文件夹的大致结构如下:
TestSkill #<- Skill
│
└─── SloganMaker #<- Function
| |
│ └─── skprompt.txt
│ └─── [config.json]
│
└─── SummarizeBlurb #<- Function
|
└─── skprompt.txt
└─── [config.json]
和自己手动定义的一样,每一个Function 都包含了一个 skprompt.txt 文件,里面就是对应的prompt,还有一个可选文件config.json 用作配置。如果有多个Skill的话,可以再往上创建一层文件夹将所有的Skill都放在里面。
然后我们在代码中仅需要将这个技能的文件夹导入到Kernel中即可。
// 这里将所有的Skill都放在了 SkillCollection 这个文件夹下
var textSkill = kernel.ImportSemanticSkillFromDirectory("./SkillCollection","TextSkill");
然后还是和往常一样正常调用即可,只不过这里导入得到的是Skill层级的,所以执行的时候需要从Skill中获取对应的Function,Function的名字和对应的文件夹名一致。
var input =
"""
Congratulations! You have imagined a delicious ASK for SK to run to completion. This ASK can be given to the Planner to get decomposed into steps. Although to make the Planner work reliably, you'll need to use the most advanced model available to you. So let's start from writing basic prompts to begin with.
""";
var resultContext = await kernel.RunAsync(input,textSkill["SummarizeBlurb"]);
resultContext.Result.Dump();
// output:
// You have imagined an ASK for SK that can be given to the Planner to be decomposed into steps. To make the Planner work reliably, you need to use the most advanced model available.
扩展自己的Semantic Function管理方式
除了官方提供的方式之外,也可以自行实现一些个性化的方便的管理方式,例如存放在文档数据库上,或者对象存储服务上,甚至使用Git、FTP等方式也不是不可以。
所需要做的只不过是将prompt和配置从远程方式获取到本地,然后通过原生的SemanticFunction注册接口注册进去就行了。
一个基本的注册方式如下:
var prompt = "A powerful Prompt"; // 对应skprompt.txt文件
var promptConfig = new PromptTemplateConfig(); //对应config.json 配置
var promptTemplate= new PromptTemplate(prompt,promptConfig,kernel);
var functionConfig = new SemanticFunctionConfig(promptConfig,promptTemplate);
var skillName = "SkillName"; // skill名称
var functionName = "FunctionName"; // function名称
var function = kernel.RegisterSemanticFunction(skillName,functionName,functionConfig);
其中的SkillName 并不是必须的,如果没有话,那默认会注册到一个名为 _GLOBAL_FUNCTIONS_ 全局技能下面,从kernel.Skills中取用的时候,如果不指定SkillName,也会从这个全局技能下获取。
只需要根据自己的喜好,处理好当前技能的管理方式,就可以打造出各种各样的个性场景了。
例如为每一个用户分配一个技能池,用户可以自行微调每个技能的相关的参数。
结合后面会提及到的Prompt Template 语法,也可以创造出更多丰富的场景。
官方Github仓库中有一个样例,就是从云端加载技能,可以大致参考一下https://github.com/microsoft/semantic-kernel/blob/main/samples/dotnet/kernel-extension-load-prompts-from-cloud/SampleExtension.cs。
Semantic Function的参数配置
除了skprompt.txt ,另外一个需要注意的就是config.json文件,也就对应着 PromptTemplateConfig 这个配置类。
一个典型的配置文件类似这样:
{
"schema": 1,
"type": "completion",
"description": "a function that generates marketing slogans",
"completion": {
"max_tokens": 1000,
"temperature": 0.0,
"top_p": 0.0,
"presence_penalty": 0.0,
"frequency_penalty": 0.0
},
"default_services": [
"text-davinci-003"
]
}
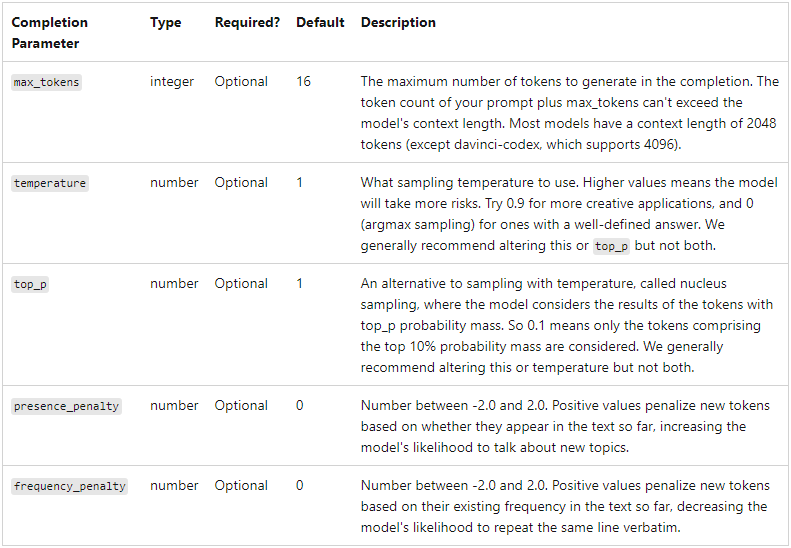
其中 schema 目前没啥用, description 提供了Function的功能说明, type 指定了当前Function的所使用的模型类型,"completion", "embeddings”之类,默认为”completion”, default_services 指定默认使用的模型名称(官方文档中还是default_backend,应该是还没来得及更新)。然后就是我们作为常见的 completion配置了。直接参考官方文档即可。
更为强大的模板语法
如果仅仅是将OpenAI的接口做了一层封装的话,其实和市面上大多数的OpenAI的sdk差不了多少,
而Semantic Kernel所能提供自然会有更多,其中就Semantic Function部分,SK就提供了一套强大的Prompt Template 语法。
变量
前面已经用到过一个最简单 {{$INPUT}} 就是SK提供的变量语法,所有的变量放在 {{ }} 中, $INPUT 就是默认的输入参数,除此之外,还可以自行定义参数。
例如:
Write me a marketing slogan for my {{$INPUT}} in {{$CITY}} with
a focus on {{$SPECIALTY}} we are without sacrificing quality.
这里的参数不区分大小写,所以有时会看到$INPUT,有时候会看到$input,都是可以的。
有了参数自然就需要能够传递多个参数进去,需要使用的是ContextVariables进行管理的。
var myContext = new ContextVariables();
myContext.Set("BUSINESS", "Basketweaving Service");
myContext.Set("CITY", "Seattle");
myContext.Set("SPECIALTY","ribbons");
var myResult = await myKernel.RunAsync(myContext,mySkill["SloganMakerFlex"]);
相比较之前直接给input运行,这里将所有参数都放在了一个ContextVariables中,打包塞进了Kernel。
函数调用
除了多个参数之外,SK还提供了类似函数调用的方式,可以在prompt中实现多种技能的组合,而且并不限制是Semantic Function 还是 Native Function。
例如有一个 weather.getForecast 的Native Function可以获取指定 city 的天气,还有一个 time.Date 可以获取今天的日期。
需要根据用户的所在城市,以及相关行程信息撰写一篇旅行日记。就可以这样写prompt:
The weather today is {{weather.getForecast $city}}.
The date is {{time.Date}}.
My itinerary for today is as follows:
===
{{ $itinerary }}
===
Generate a travel diary based on the above content.
除此之外,模板语法的还有一些符号转义的注意事项,可以具体参考Github中的文档https://github.com/microsoft/semantic-kernel/blob/main/docs/PROMPT_TEMPLATE_LANGUAGE.md。
至此,Semantic Function的基本配置和使用的掌握的差不多了。
参考资料:
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/semantic-kernel/howto/semanticfunctions
- https://github.com/microsoft/semantic-kernel/tree/main/samples/dotnet/kernel-extension-load-prompts-from-cloud
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/semantic-kernel/howto/configuringfunctions
- https://github.com/microsoft/semantic-kernel/blob/main/dotnet/src/SemanticKernel/SemanticFunctions/PromptTemplateConfig.cs
- https://github.com/microsoft/semantic-kernel/blob/main/docs/PROMPT_TEMPLATE_LANGUAGE.md